Self-hosting n8n gives you full control over your workflow automation while keeping your data secure and costs effective. This complete guide walks you to Self-host n8n, from choosing your hosting method to advanced configurations.
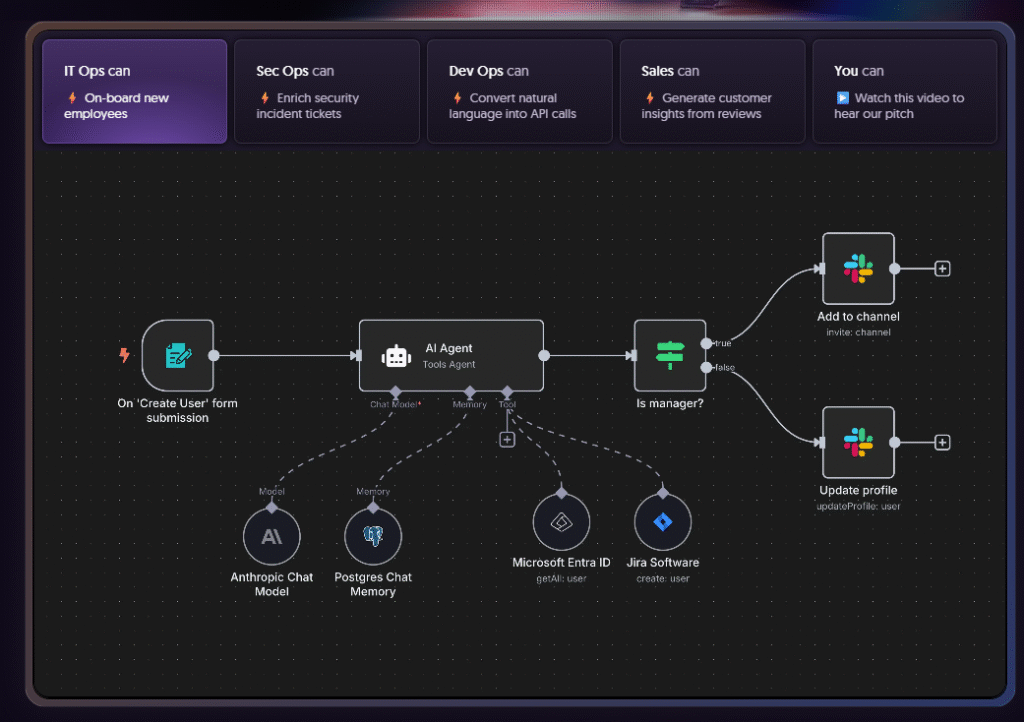
What is n8n and Why Self-Host n8n?
What is n8n? n8n is an open-source workflow automation tool that connects different applications and services without requiring coding knowledge. It’s like Zapier but with more flexibility and customization options, and it’s easy to use.
Why Choose Self-Hosting Over Cloud Services?
Complete Data Control: Your business data never leaves your servers, ensuring maximum privacy and compliance with data protection regulations and full control over data.
Low Cost: Self-hosting eliminate monthly subscription fees, making it ideal for businesses with high automation volumes or tight budgets.
Unlimited Customization: Install custom nodes, modify the interface, and integrate with internal systems without platform restrictions.
No Workflow Limitations: Run unlimited workflows with unlimited executions, unlike cloud services that impose usage caps.
Prerequisites and System Requirements
What Do You Need Before Starting?
Minimum System Requirements:
- 2 GB RAM (4 GB recommended)
- 2 CPU cores
- 10 GB available storage
- Ubuntu 20.04+ or similar Linux distribution
- Basic command line knowledge
Required Software:
- Docker and Docker Compose (recommended method)
- Node.js 18+ (for npm installation)
- PostgreSQL or MySQL (for production use)
- Nginx or Apache (for reverse proxy)
Technical Prerequisites:
Text editor familiarity (nano, vim, or VS Code)
Domain name with DNS access
SSL certificate capability
Basic understanding of server administration
Method 1: Docker Installation (Recommended)
Step 1: Install Docker and Docker Compose
Why is Docker the best choice for beginners? Docker simplifies installation, ensures consistency across environments, and makes updates effortless while isolating n8n from your system.
bash
# Update system packages
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
# Install Docker
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
sudo sh get-docker.sh
# Add user to docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
# Install Docker Compose
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.24.0/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
# Verify installation
docker --version
docker-compose --versionStep 2: Create Docker Compose Configuration
Create a directory for your n8n installation:
bash
mkdir ~/n8n-docker
cd ~/n8n-dockerCreate a docker-compose.yml file:
yaml
version: '3.8'
services:
n8n:
image: n8nio/n8n
restart: always
ports:
- "5678:5678"
environment:
- GENERIC_TIMEZONE=UTC
- TZ=UTC
- N8N_SECURE_COOKIE=false
- WEBHOOK_URL=https://your-domain.com/
- N8N_HOST=your-domain.com
- N8N_PORT=5678
- N8N_PROTOCOL=https
volumes:
- n8n_data:/home/node/.n8n
depends_on:
- postgres
postgres:
image: postgres:15
restart: always
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=n8n
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=your_secure_password
- POSTGRES_DB=n8n
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
n8n_data:
postgres_data:Step 3: Launch n8n
bash
# Start services
docker-compose up -d
# Check if services are running
docker-compose ps
# View logs if needed
docker-compose logs n8nAccess your n8n instance by navigating to http://your-server-ip:5678 in your browser.
Method 2: Direct Installation with npm
When should you use npm installation? Choose this method when you need more control over the Node.js environment or want to integrate n8n with existing Node.js applications.
Step 1: Install Node.js and npm
bash
# Install Node.js 18.x
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
# Verify installation
node --version
npm --versionStep 2: Install n8n Globally
bash
# Install n8n
sudo npm install -g n8n
# Create n8n user and directory
sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash n8n
sudo mkdir -p /home/n8n/.n8n
sudo chown -R n8n:n8n /home/n8n/.n8nStep 3: Create Systemd Service
Create a service file at /etc/systemd/system/n8n.service:
ini
[Unit]
Description=n8n workflow automation
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=n8n
ExecStart=/usr/bin/n8n start
WorkingDirectory=/home/n8n
Environment=N8N_BASIC_AUTH_ACTIVE=true
Environment=N8N_BASIC_AUTH_USER=admin
Environment=N8N_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD=your_secure_password
Environment=WEBHOOK_URL=https://your-domain.com/
Environment=GENERIC_TIMEZONE=UTC
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetStep 4: Start and Enable Service
bash
# Reload systemd
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# Enable and start n8n
sudo systemctl enable n8n
sudo systemctl start n8n
# Check status
sudo systemctl status n8nMethod 3: Cloud VPS Setup
Choosing the Right VPS Provider
Which cloud provider offers the best value? Consider these popular options:
DigitalOcean: Excellent documentation, predictable pricing, and n8n-optimized droplets starting at $6/month.
Linode: Competitive pricing with excellent performance, ideal for CPU-intensive workflows.
AWS EC2: Most flexible but complex pricing structure, best for enterprise deployments.
Hetzner: European provider with exceptional price-to-performance ratio.
VPS Configuration Steps
- Choose Your Server Size: Start with 2 GB RAM, 1 vCPU for testing, scale to 4 GB RAM, 2 vCPU for production.
- Select Operating System: Ubuntu 22.04 LTS provides the best compatibility and long-term support.
- Configure SSH Access: Use SSH keys instead of passwords for enhanced security.
- Set Up Firewall Rules:
bash
sudo ufw default deny incoming
sudo ufw default allow outgoing
sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw allow 80
sudo ufw allow 443
sudo ufw enable- Follow Docker Installation Steps from Method 1 above.
Essential Configuration Settings
Environment Variables Explained
What are the most important n8n environment variables? Here are the critical settings you need to configure:
bash
# Security Settings
N8N_BASIC_AUTH_ACTIVE=true
N8N_BASIC_AUTH_USER=your_username
N8N_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD=your_secure_password
# URL Configuration
WEBHOOK_URL=https://your-domain.com/
N8N_HOST=your-domain.com
N8N_PROTOCOL=https
N8N_PORT=5678
# Database Configuration
DB_TYPE=postgresdb
DB_POSTGRESDB_HOST=postgres
DB_POSTGRESDB_PORT=5432
DB_POSTGRESDB_DATABASE=n8n
DB_POSTGRESDB_USER=n8n
DB_POSTGRESDB_PASSWORD=your_db_password
# Execution Settings
EXECUTIONS_PROCESS=main
EXECUTIONS_DATA_SAVE_ON_ERROR=all
EXECUTIONS_DATA_SAVE_ON_SUCCESS=all
EXECUTIONS_DATA_MAX_AGE=336
# Timezone Settings
GENERIC_TIMEZONE=America/New_York
TZ=America/New_YorkDatabase Configuration
Should you use PostgreSQL or MySQL? PostgreSQL is recommended for production environments due to better JSON support and performance with complex workflows.
SQLite vs PostgreSQL: SQLite works for development and small deployments, but PostgreSQL handles concurrent executions and large datasets much better.
Security Best Practices
Authentication and Access Control
How do you secure your n8n installation? Implement these essential security measures:
1. Enable Basic Authentication:
bash
N8N_BASIC_AUTH_ACTIVE=true
N8N_BASIC_AUTH_USER=admin
N8N_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD=ComplexPassword123!2. Use Strong Passwords: Generate passwords with at least 16 characters including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols.
3. Restrict Network Access:
bash
# Only allow specific IP addresses
sudo ufw allow from YOUR_IP_ADDRESS to any port 5678SSL/TLS Configuration
Why is HTTPS mandatory for n8n? Many modern APIs require HTTPS endpoints for webhooks, and browsers block mixed content, making SSL essential for reliable operation.
Setting up Let’s Encrypt with Certbot:
bash
# Install Certbot
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx
# Get certificate
sudo certbot --nginx -d your-domain.com
# Auto-renewal
sudo crontab -e
# Add: 0 12 * * * /usr/bin/certbot renew --quietDatabase Setup and Management
PostgreSQL Setup for Production
Why use PostgreSQL over SQLite? PostgreSQL provides better concurrent access, data integrity, and performance for production workloads.
bash
# Install PostgreSQL
sudo apt update
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
# Create database and user
sudo -u postgres psql
CREATE DATABASE n8n;
CREATE USER n8n WITH PASSWORD 'your_secure_password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE n8n TO n8n;
\qDatabase Maintenance
How often should you backup your n8n database? Daily backups are recommended for production environments, with weekly full backups and point-in-time recovery capabilities.
Backup Script Example:
bash
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/home/n8n/backups"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
# Create backup directory
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR
# Backup PostgreSQL database
pg_dump -h localhost -U n8n n8n > $BACKUP_DIR/n8n_backup_$DATE.sql
# Keep only last 7 days of backups
find $BACKUP_DIR -name "n8n_backup_*.sql" -mtime +7 -deleteSetting Up SSL Certificates
Nginx Reverse Proxy Configuration
What’s the best way to serve n8n securely? Use Nginx as a reverse proxy with SSL termination for optimal security and performance.
Create /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8n:
nginx
server {
listen 80;
server_name your-domain.com;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name your-domain.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your-domain.com/privkey.pem;
# SSL Security Headers
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff always;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5678;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# WebSocket support
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
}Enable the site:
bash
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/n8n /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginxBackup and Maintenance
Automated Backup Strategy
What should you backup in n8n? Your backup strategy should include workflow data, credentials, settings, and execution history.
Complete Backup Script:
bash
#!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backups/n8n"
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
BACKUP_NAME="n8n_full_backup_$DATE"
mkdir -p $BACKUP_DIR/$BACKUP_NAME
# Backup database
docker exec n8n_postgres_1 pg_dump -U n8n n8n > $BACKUP_DIR/$BACKUP_NAME/database.sql
# Backup n8n data directory
docker cp n8n_n8n_1:/home/node/.n8n $BACKUP_DIR/$BACKUP_NAME/n8n_data
# Create compressed archive
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/$BACKUP_NAME.tar.gz -C $BACKUP_DIR $BACKUP_NAME
rm -rf $BACKUP_DIR/$BACKUP_NAME
# Upload to cloud storage (optional)
# aws s3 cp $BACKUP_DIR/$BACKUP_NAME.tar.gz s3://your-backup-bucket/Update Management
How do you safely update n8n? Always backup before updating and follow a staged deployment approach.
bash
# Backup before updating
./backup_script.sh
# Pull latest Docker image
docker-compose pull
# Restart with new image
docker-compose down
docker-compose up -d
# Check logs for issues
docker-compose logs -f n8nTroubleshooting Common Issues
Connection Problems
Why can’t I access my n8n installation? Common connection issues and their solutions:
Port Binding Issues:
bash
# Check if port is in use
sudo netstat -tlnp | grep :5678
# Kill process using port
sudo kill -9 PID_NUMBERFirewall Blocking Access:
bash
# Check UFW status
sudo ufw status
# Allow n8n port
sudo ufw allow 5678Performance Issues
Why are my workflows running slowly? Performance problems often stem from insufficient resources or database configuration.
Memory Issues:
bash
# Check memory usage
free -h
docker stats
# Increase Docker memory limit
# Add to docker-compose.yml:
# mem_limit: 2gDatabase Performance:
bash
# Check PostgreSQL connections
sudo -u postgres psql -c "SELECT * FROM pg_stat_activity;"
# Optimize PostgreSQL settings in postgresql.conf:
shared_buffers = 256MB
effective_cache_size = 1GB
work_mem = 4MBWorkflow Execution Errors
What causes workflow execution failures? Common issues include timeout errors, API rate limits, and credential problems.
Timeout Configuration:
bash
# Increase timeout limits
N8N_DEFAULT_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT=300
N8N_MAX_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT=3600Debug Mode:
bash
# Enable debug logging
N8N_LOG_LEVEL=debugPerformance Optimization
Resource Allocation
How much RAM does n8n need? Resource requirements depend on workflow complexity and execution frequency:
- Light Usage (< 10 workflows, simple operations): 2 GB RAM, 1 CPU
- Medium Usage (10-50 workflows, API integrations): 4 GB RAM, 2 CPUs
- Heavy Usage (50+ workflows, data processing): 8 GB RAM, 4 CPUs
Execution Settings
What are the best execution settings for performance? Configure these environment variables for optimal performance:
bash
# Execution settings
EXECUTIONS_PROCESS=main
EXECUTIONS_MODE=queue
QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_HOST=redis
QUEUE_BULL_REDIS_PORT=6379
# Worker settings
N8N_WORKERS_COUNT=4
N8N_WORKER_TIMEOUT=60
# Memory management
NODE_OPTIONS=--max-old-space-size=4096Database Optimization
How do you optimize database performance? Regular maintenance and proper indexing significantly improve performance:
sql
-- Analyze database statistics
ANALYZE;
-- Reindex tables
REINDEX DATABASE n8n;
-- Clean up old executions
DELETE FROM execution_entity WHERE "startedAt" < NOW() - INTERVAL '30 days';Frequently Asked Questions
General Questions
Is self-hosting n8n free?
Yes, n8n is open-source and free to self-host. You only pay for your hosting infrastructure costs.
Can I migrate from n8n Cloud to self-hosted?
Yes, you can export your workflows from n8n Cloud and import them into your self-hosted instance. However, execution history doesn’t transfer.
How do I update my self-hosted n8n instance?
For Docker installations, pull the latest image with docker-compose pull then restart your services. Always backup first.
What’s the difference between SQLite and PostgreSQL for n8n?
SQLite is suitable for development and small deployments, while PostgreSQL is recommended for production use due to better performance and concurrent access handling.
Can I run multiple n8n instances?
Yes, you can run multiple instances for high availability, but you’ll need to share the same database and configure load balancing properly.
How do I secure my n8n installation?
Enable HTTPS, use strong authentication, restrict network access, keep software updated, and regularly backup your data.
Why are my webhooks not working?
Ensure your WEBHOOK_URL environment variable is set correctly with HTTPS, and your domain is publicly accessible with proper DNS configuration.
My workflows fail with timeout errors. What should I do?
Increase timeout settings with N8N_DEFAULT_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT and N8N_MAX_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT environment variables, and consider optimizing your workflow logic.
How do I recover from a corrupted database?
Restore from your most recent backup. If no backup exists, you may need to recreate workflows manually. This emphasizes the importance of regular backups.
Conclusion
Self-hosting n8n provides complete control over your workflow automation while maintaining data privacy and reducing costs. Whether you choose Docker for simplicity or direct installation for flexibility, following this guide ensures a secure, performant, and maintainable n8n deployment.
Remember to implement proper security measures, maintain regular backups, and monitor your instance’s performance. As your automation needs grow, you can scale your infrastructure accordingly while maintaining the benefits of self-hosting.
Start with the Docker method if you’re new to self-hosting, then gradually implement advanced features like SSL certificates, database optimization, and automated backups as you become more comfortable with the platform.



[…] Blog […]
[…] Blog […]